Proof of Why sin 0 = 0
Hello friends, welcome back to the blog "Ibnu Batauga"! In this article, we will discuss one of the trigonometric functions that we often encounter: sine ($\sin$). More specifically, we will prove why $\sin 0 = 0$. Let’s learn it together in an easy-to-understand way.
Definition of the Sine Function
The sine function ($\sin$) is one of the basic functions in trigonometry that is related to right triangles. In a right triangle, $\sin$ of an angle is the ratio between the length of the side opposite the angle and the length of the hypotenuse.
Visualization on the Unit Circle
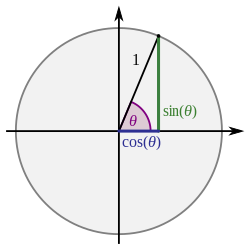
To make it easier to understand, we can use the unit circle (a circle with radius 1). On the unit circle, the angle 0 degrees (or 0 radians) is located at the point $(1, 0)$ on the $x$-axis.
Using the Definition of Sine on the Unit Circle
In the context of the unit circle, the $\sin$ function of an angle $\theta$ is the $y$-coordinate of the point on the circle that corresponds to that angle. So, for the angle 0 degrees (0 radians), we look at the point $(1, 0)$.
- The $x$-coordinate of this point is 1.
- The $y$-coordinate of this point is 0.
Because $\sin \theta$ is the $y$-coordinate of the point on the unit circle corresponding to the angle $\theta$, then $\sin 0$ is the $y$-coordinate of the point $(1, 0)$, which is 0.
Explanation Using a Right Triangle
We can also use the concept of a right triangle to prove $\sin 0 = 0$. Imagine we have a right triangle with an angle that is very small, approaching 0 degrees. As the angle becomes 0, the length of the side opposite that angle also approaches 0. Since $\sin \theta$ is the ratio between the length of the opposite side and the hypotenuse, when the angle $\theta = 0$, the length of the opposite side is 0, so:
$\sin 0 = \frac{0}{\text{hypotenuse}} = 0$
Using the Taylor Series
Another way to prove $\sin 0 = 0$ is by using the Taylor series. The Taylor series for the function $\sin(x)$ around $x = 0$ is:
$\sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \cdots$
If we substitute $x = 0$ into this series:
$\sin(0) = 0 - \frac{0^3}{3!} + \frac{0^5}{5!} - \cdots = 0$
So, this also shows that $\sin 0 = 0$.
Conclusion: Sin 0
Now we know that $\sin 0 = 0$ can be proven in several ways, whether through the unit circle, right triangles, or the Taylor series. All of these methods lead to the same conclusion, namely $\sin 0 = 0$.
Hopefully, this explanation helps you better understand this trigonometric concept. Don’t forget to stay motivated in learning mathematics, and see you in the next article on "Ibnu Batauga"!
Information: I just created a number factorization calculator, please click Integer Factor Calculator.


Post a Comment for "Proof of Why sin 0 = 0"